Tel: +86-532-84673097
Mobile & Whatsapp & Wechat:+86-13589340409
Mobile & Whatsapp & Wechat:+86-13589340409
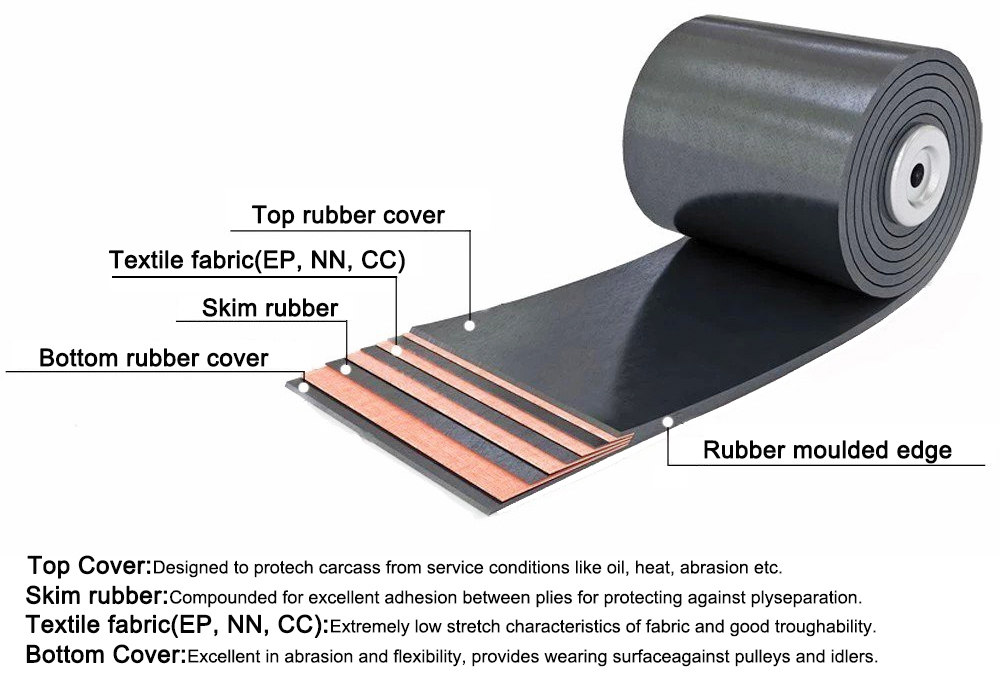
Lower elongation in the warp direction and excellent troughability in the weft direction
Excellent resistance to moisture, wet, and mildew
Excellent resistance to impact and wear
Good resistance to chemicals and corrosion
Strong adhesion between the carcass layers and the rubber cover
High tensile strength and good elasticity
Excellent resistance to acid, alkali, and heat
Provide a long working life
Economical and eco-friendly
| Fabric Type | Fabric Specification | Fabric Layer Thickness (mm) | Fabric Strength (N/mm) | Covering Layer Thickness (mm) | Width (mm) | Length (m) | |||
| 2 Layer | 3 Layer | 4 Layer | Top Layer | Bottom Layer | |||||
| EP/Polyester | EP-80 | 1.00 | 160 | 240 | 320 | 2.0-8.0 | 0-4.5 | 300-2000 | 20-300 |
| EP-100 | 1.00 | 200 | 300 | 400 | |||||
| EP-125 | 1.05 | 250 | 375 | 500 | |||||
| EP-150 | 1.10 | 300 | 450 | 600 | |||||
| EP-170 | 1.15 | 340 | 510 | 680 | |||||
| EP-200 | 1.20 | 400 | 600 | 800 | |||||
| EP-250 | 1.40 | 500 | 750 | 1000 | |||||
| EP-300 | 1.60 | 600 | 900 | 1200 | |||||
| EP-350 | 1.70 | 1050 | 1400 | ||||||
| EP-400 | 1.90 | 1600 | |||||||
| EP-500 | 2.10 | 2000 | |||||||
| Adhesion and Elongation | |||||
| Carcass | Adhesion | Elongation at break | |||
| Interlayer N/mm | N/mm between rubber and carcass | Longitudinal elongation at break | Longitudinal reference elongation | ||
| Rubber thickness ≤1.5mm | Rubber thickness >1.5mm | ||||
| EP/Polyester Canvas | ≥4.50 | ≥3.2 | ≥3.5 | ≥10% | ≤4% |
| Cover Performance of EP Conveyor Belt | |||||
| Cover Level | Tensile strength | Elongation at break | Abrasion | Change rate of tensile strength and elongation at break after aging | |
| ≥ | ≥ | ≤ | |||
| Mpa | Kgf/cm² | % | mm³ | % | |
| Heavy | 24 | 240 | 450 | 120 | -25 ~ +25 |
| Medium | 18 | 180 | 400 | 100 | -25 ~ +25 |
| Light | 15 | 150 | 350 | 200 | -30 ~ +30 |
1. How do EP Conveyor Belts compare to traditional rubber belts?
EP conveyor belts offer superior durability, temperature resistance, and tensile strength compared to traditional rubber belts, making them ideal for handling heavy loads and operating in extreme conditions. They are more flexible, allowing for tighter bends and efficient use of space, and provide better resistance to chemicals, oils, and fats.
2. What are the Benefits of EP Conveyor Belts for Heavy-Duty Applications?
EP conveyor belts are made from a blend of polyester and nylon fibers, which provides exceptional tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, tearing, and impact. Their high flexibility and low elongation under tension make them ideal for handling heavy loads over long distances. Additionally, EP conveyor belts maintain their structural integrity and performance even in harsh environments, contributing to increased operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. Their versatility and robustness make them a preferred choice for industries such as mining, construction, and manufacturing.
3. How to choose the number of layers of EP fabric conveyor belt? Is the more layers of EP conveyor the better?
Choosing the number of layers for an EP (polyester/nylon) fabric conveyor belt requires careful consideration of load capacity, belt length, flexibility, and the operating environment. While more layers can enhance the belt’s strength and load-carrying capacity, making them suitable for heavy loads and long conveyors, too many layers can reduce flexibility and increase the risk of fiber breakage due to heightened flexural tension. Excessive layers lead to increased tension on the carcass fiber, which can cause premature damage, even if the belt has high tear strength. For applications needing high flexibility or operating under mild conditions, fewer layers may be more cost-effective and appropriate. Optimal performance is achieved by matching the number of layers to the specific demands of the application and enhancing flexibility through adjustments like increasing skim rubber thickness, rather than simply adding more layers.
